Main page (Russian)
 Search in database (English)
Search in database (English)
Properties of substance:
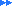
nitrobenzene
skc-fileGroup of substances:
organic
Physical appearance:
colorless oily liquidEmpirical formula (Hill's system for organic substances):
C6H5NO2Structural formula as text:
C6H5NO2Molar/atomic mass: 123.10995
Melting point (°C):
5.76Boiling point (°C):
210.9Solubility (g/100 g of solvent):
ammonia liquid : 31.6 (20°C) [Ref.]
benzene: very soluble [Ref.]
deuterium oxide: 0.1445 (6°C) [Ref.]
deuterium oxide: 0.1685 (30°C) [Ref.]
deuterium oxide: 0.213 (50°C) [Ref.]
diethyl ether: soluble [Ref.]
ethanol: soluble [Ref.]
hydrogen fluoride : very soluble [Ref.]
sulfur dioxide: 100 (20°C) [Ref.]
water: 0.19 (20°C) [Ref.]
water: 0.312 (60°C) [Ref.]
Numerical data:
Sweetness potency сompared with a 2% (w/v) aqueous solution of sucrose: 95
Density:
1.2231 (0°C, g/cm3)
1.2082 (15°C, g/cm3)
1.1986 (25°C, g/cm3)
1.1934 (30°C, g/cm3)
Synthesis 1:
Reference: Гитис С.С., Глаз А.И., Иванов А.В. Практикум по органической химии: Органический синтез. - М.: Высшая школа, 1991 pp. 108-10911 ml of concentrated nitric acid is poured into a round-bottom flask. 13 ml of concentrated sulfuric acid is added with shaking and outside cooling with cold water. After cooling of the nitration mixture until room temperature 10 ml of benzene is added per 1 ml with constant shaking. After ending up addition of benzene the flask is closed by a cork with air condenser and the contents of the flask is heated on a water bath at 60 C (temperature of water into the bath) for 30 minutes with frequent shaking of the reaction mixture and harsh sustaining of temperature of the reaction.
After ending of the process the flask is cooled with water until room temperature and the contents are poured into a separatory funnel. The lower (acidic) layer is drained away and the upper layer (nitrobenzene) is rinsed gradually with water, 5% solution of sodium hydroxide (for neutralisation of remaining acids) and againg with water. During these operations nitrobenzene remains in the lower layer. After rinsing nitrobenzene is drained into a dry flask and fused calcium chloride is added. The flask is closed by a cork with air condenser and heated on a boiling water bath until the liquid becomes clear. It is poured into a wurtz flask (without calcium chloride) and distilled with air condenser, the fraction with boiling point at 207-211 C is collected. It is forbidden to distill nitrobenzene until dryness in order to prevent the explosive decomposition of a side product of the reaction - m-dinitrobenzene.
The yield is 11 gr (81% from theory).
Reactions of synthesis:
- Yeild 80-95%. [Ref.1]
C6H6 + NO2BF4 → C6H5NO2 + HBF4
- Yeild 85-86%. [Ref.1]
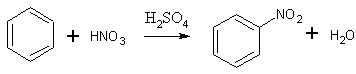
Refractive index (nD):
1.55457 (15°C)
1.55257 (20°C)
Dissociation:
pKBH+ (1) = -12.14 (25°C, water)
Permittivity (dielectric constant):
34.82 (30°C)
20.8 (130°C)
Dipole moment (D):
4.22 (20°C)
Standard molar enthalpy (heat) of formation ΔfH0 (298.15 K, kJ/mol):
11.2 (l)Standard molar entropy S0 (298.15 K, J/(mol·K)):
224.3 (l)Molar heat capacity at constant pressure Cp (298.15 K, J/(mol·K)):
177.27 (l)Molar enthalpy (heat) of fusion ΔfusH (kJ/mol):
11.59Enthalpy (heat) of vaporization ΔvapH (kJ/mol):
40.79Flash point (°C):
83Autoignition temperature (°C):
482Heat of combustion (kJ/mol):
3092.8LD50 (mg/kg):
550 (white mice, oral)
600 (rabbits, oral)
600 (rats, oral)
References:
- Olah G.A., Prakash G.K.S., Molnar A., Sommer J. Superacid chemistry. - 2ed. - Wiley, 2009. - pp. 14
- Seidell A. Solubilities of organic compounds. - 3ed., vol.2. - New York: D. Van Nostrand Company, 1941. - pp. 356-360
- Urbanski T. Chemistry and technology of explosives. - vol.1. - Warszawa, 1964. - pp. 230-233
- Yalkowsky S.H., Yan H. Handbook of aqueous solubility data. - CRC Press, 2003. - pp. 229
- Вредные вещества в промышленности: Справочник для химиков, инженеров и врачей. - 7-е изд., Т.2. - Л.: Химия, 1976. - pp. 253-254 [Russian]
- Гитис С.С., Глаз А.И., Иванов А.В. Практикум по органической химии: Органический синтез. - М.: Высшая школа, 1991. - pp. 109 [Russian]
- Рабинович В.А., Хавин З.Я. Краткий химический справочник. - Л.: Химия, 1977. - pp. 166 [Russian]
- Справочник по растворимости. - Т.1, Кн.1. - М.-Л.: ИАН СССР, 1961. - pp. 430-431, 908 [Russian]
- Справочник по растворимости. - Т.1, Кн.2. - М.-Л.: ИАН СССР, 1962. - pp. 967, 1399 [Russian]
What information do you need?
© Collected Ruslan Anatolievich Kiper, burewestnik@mail.ru

